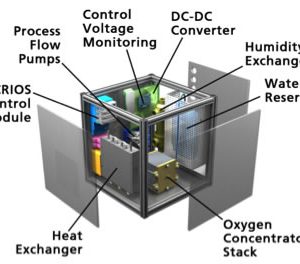
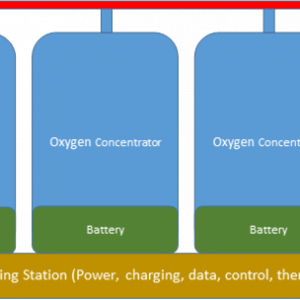
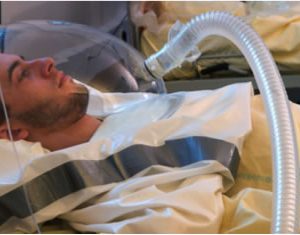
Oxygen Concentrator Module
The Challenge
A system is needed to deliver oxygen to crew members in flight while minimizing local and cabin oxygen build-up. An oxygen concentrator that provides a source of enriched oxygen from spacecraft cabin air for use in spacecraft emergencies that can be deployed rapidly, is portable and eliminates the possibility of a buildup of enriched oxygen is necessary to for long mission space exploration. A very ill crewmember requires a significant flow of oxygen, up to 15 LPM, but lower flow rates may be adequate for less ill crewmembers or as respiratory supply for healthy crew. To address these multiple flow ranges, a redundant set of lower flow concentrators is envisioned that could be used separately as needed (at 3-4 LPM) or combined for the high flow need. The lower flow modules can be run off batteries for a reasonable period of time or plugged in if the crew is relatively stationary.
The Research
NASA has analyzed the oxygen concentration that would be in the crew exploration vehicle by comparing it to the US Lab on the International Space Station using the continuously stirred tank reactor model.
There are several medical conditions that require oxygen support, including smoke inhalation, sepsis, hypovolemic shock, medication overdose, chest injury, cardiac arrest, and several others. Another possible application for the oxygen concentrator is use in a portable mode at 3-4 LPM as an option for pre-breathing protocol by the crew in preparation for Extravehicular Activities (EVA) and to protect healthy crewmembers if there is an atmospheric contamination event such as a toxic spill or a fire, to avoid toxic gas or smoke inhalation.
The Progress
Developing an oxygen concentrator with high energy efficiency and a feedback system to maintain the proper tissue oxygenation level to reduce caregiver involvement are both highly desired attributes for an exploration spaceflight mission. NASA Glenn Research Center validated performance of an OCM technology for transition to NASA’s environmental and life support team (ELCSS) for them to integrate into testbeds for further evaluation.
To integrate the OCM with the patient care system, NASA GRC developed requirements and a concept of operation for a system level approach to supplemental oxygen with the Medical Oxygen Patient Interface (MOPI), which will provide the necessary interfaces to other sub-systems that are being planned for a vehicle or surface platform. The planned multifaceted suite will include:
– Patient to MOPI interface comprising of oxygen-enriched air provided to the patient via mask, cannula, or intubation/ventilator, as well as receiving, displaying, and storing patient physiological sensor data output comprising parameters such as blood O2 saturation levels O2, respiratory rate, and core temperature.
– Caregiver to MOPI interface comprising a dashboard with data such as gas flow rate and gas oxygen concentration level and control via a keypad, gestures and/or voice
– Vehicle to MOPI interface comprising oxygen-enriched air, OCM health & status output, and command inputs to treatment variables
– Medical System to MOPI interface comprising patient sensor and caregiver command data as inputs to record in the patient medical history file and clinical decision support output
Acronyms
EVA – Extravehicular Activities
GRC – Glenn Research Center
ISS – International Space Station
LPM – Liters Per Minute
MOPI – Medical Oxygen Patient Interface
NASA – National Aeronautics and Space Administration
NSBRI – National Space Biomedical Research Institute
OCM – Oxygen Concentrator Module
SBIR – Small Business Innovation Research
US LAB – United States Laboratory
Technical Data
- Evaluation of the Oxygen Concentrator Prototypes: Pressure Swing Adsorption Prototype and Electrochemical Prototype
- Development of an Oxygen Concentrator for Future Exploration Missions
- Oxygen Concentrator Model Architecture
Oxygen Concentrator Module Gaps
What is an HRP Gap?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please select the links below the for more information.
Gallery
Cardiovascular Impacts
What are the in-flight alterations in cardiac structure and function?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Measuring VO2 inflight
What is VO2max in-flight and immediately post-flight?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Predicting Heart Disease
Can manifestations of sub-clinical or environmentally induced cardiovascular diseases during spaceflight be predicted?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Outcome of Medical Events
We do not know the quantified health and mission outcomes due to medical events during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Doctor on Board?
We do not know how the inclusion of a physician crew medical officer quantitatively impacts medical risk during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Microgravity Countermeasures
How does 1/6-g and 3/8-g influence countermeasures?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Efficient Exercise Regimen
Develop the most efficient and effective exercise program for the maintenance of muscle function.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Minimum Exercise Needed?
What is the minimum exercise regimen needed to maintain fitness levels for tasks?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Exercise Hardware
Identify and validate exploration countermeasure hardware for the maintenance of muscle function.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Time Course of Changes in Muscle
Characterize the time course of changes in muscle protein turnover, muscle mass, and function during long duration space flight.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Bone Health Standard
A new acceptable bone health standard using an expanded surrogate for bone health needs to be defined for the flight environment.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Osteoporosis & Fractures
What is the incidence & prevalence of early onset osteoporosis or fragility fractures due to exposure to spaceflight.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Ocular changes
We do not know the etiological mechanisms and contributing risk factors for ocular structural and functional changes seen in-flight and post-flight.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Medical Event Risk Metrics
We need to characterize the medical conditions that can occur during exploration missions and their relevant associated end states, management options, and the capabilities necessary to manage them (what can happen, how bad could it be, what can we do to improve it?).
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Integrated Exploration Medical System Models
We need to develop integrated exploration medical system models for the Moon and Mars.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Cardiovascular Impacts from Weightlessness
Determine whether long-duration weightlessness induces cardiovascular structural and functional changes and/or oxidative stress & damage (OSaD)/inflammation, that can contribute to development of disease.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Fluid Intake
Is it necessary to increase crew fluid intake and, if possible, to what extent will it mitigate stone formation?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Frequency of formation
What is the frequency of post-flight stone formation; the incidence and types of stones; and the time course of stone formation? How does stone formation correlate with food intake and hydration status?
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Medical Imaging
We do not have the capability to provide non-invasive medical imaging during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Back/Neck Injury
Limited capability to treat back/neck pain and injuries in the space flight environment
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Provide Oxygen to Crew
We do not have the capability to deliver supplemental oxygen to crew members while minimizing local and cabin oxygen build-up during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Bone Fractures
We do not have the capability to stabilize bone fractures and accelerate fracture healing during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Medical Suction
We do not have the capability to provide medical suction and fluid containment during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
IV Fluids
We do not have the capability to generate and utilize sterile intravenous fluid from potable water during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Renal Stones
We have limited capability to screen for, diagnose, and treat renal stones during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.
Medical Inventory
We do not have the capability to track medical inventory in a manner that integrates securely with the medical system during exploration missions.
Evidence from medical records, spaceflight operations and research findings provides the basis for identifying the most significant human risks in space exploration, including physiological and performance effects from hazards such as altered gravity, radiation, hostile/closed environments, isolation and distance. Each risk is assigned to an HRP Element (divisions of human research) to identify knowledge gaps, or the critical questions that must be answered, in order to mitigate the risk. These gaps become the focus of research conducted to reduce the likelihood and consequence of risks becoming a reality. To learn more about the Risk Identification and Mitigation process and the tasks developed to reduce those risks for the program please click on the link below the gap for more information.